
When using optimset, you can change the précision of the solution, and the parameter 0 in fsolve is the x0 for the solution. Create a cylinder defined by the profile function 2 + cos (t). The direction field solver knows about trigonometric, logarithmic and exponential functions, but multiplication and evaluation must be entered explicitly ( 2x and sin (x), not 2x and sin x ). In this case, y is a function and you can use y(5) to evaluate it value. Create a cylinder and use the returned coordinates to plot multiple cylinders in different locations. For a much more sophisticated phase plane plotter, see the MATLAB plotter written by John C.

You can defined a function using by writing: y = i*sqrt((((w^2*Mr*(Er))/isik_hizi^2)-(2*pi/lamdac)^2)) The toolbox provides the following models for mapping your input to output: Linear polynomial curve, Linear polynomial surface, Quadratic polynomial cu, Local linear regression (surface) But however for multivariate (more than 3 input) linear fits, you can use the statistics toolbox.
#MATLAB EQUATION MAKER CODE#
This is done in the third line of code for the b variable. What the code is doing is converting dB values to its respective magnitude ranging from 0dB to 20dB in increments of 0.5dB.
#MATLAB EQUATION MAKER UPDATE#
Mr= (1+yansima1)/(v*(1-yansima1)*sqrt((1/lamda0)^2-(1/lamdac)^2)) I need to update a simple Matlab code shown below. S21 = gecis_genlik*cosd(gecis_faz)+i*gecis_genlik*sind(gecis_faz) %gecis_genlik= input('Genliği giriniz =')

C nchoosek (v,k) returns a matrix containing all possible combinations of the elements of vector v taken k at a time. This is the number of combinations of n items taken k at a time. S11 = yansima_genlik*cosd(yansima_faz)+i*yansima_genlik*sind(yansima_faz) b nchoosek (n,k) returns the binomial coefficient, defined as. % yansima_genlik= input('Genliği giriniz =') Using our calculator is as simple as copying and pasting the corresponding X and Y values into the table (don't forget to add labels for the variable names). I know other parameters and they are complex (w, Mr, isik_hizi, etc.) This calculator is built for simple linear regression, where only one predictor variable (X) and one response (Y) are used. ^) is very important.I have a equation but how I will find roots of function? operator in front of the exponentiation operator (i.e. Take special note that I assumed the function will element-wise square each elements in the input. (y-2)).2)-5 radius of the sphere position on x axis. im showing an example for one function could be. Let's say I want to create a function that squares every element in the input: > func = input('f(x) = ', 's') im new here but i did made some for matlab without using sphere function although with fmesh divide the sphere in 2 parts and use 2 functions to plot on positive and one negative. Take note that I had to concatenate the anonymous function string with the inputted function you provided with input. You'll want to take the input as a string by using the 's' option as the second parameter then use str2func to convert the string into an anonymous function: func = input('f(x) = ', 's') Bear in mind that the default method of input is to directly take the input and assign it as a variable where the input is assumed to be syntactically correct according to MATLAB rules.

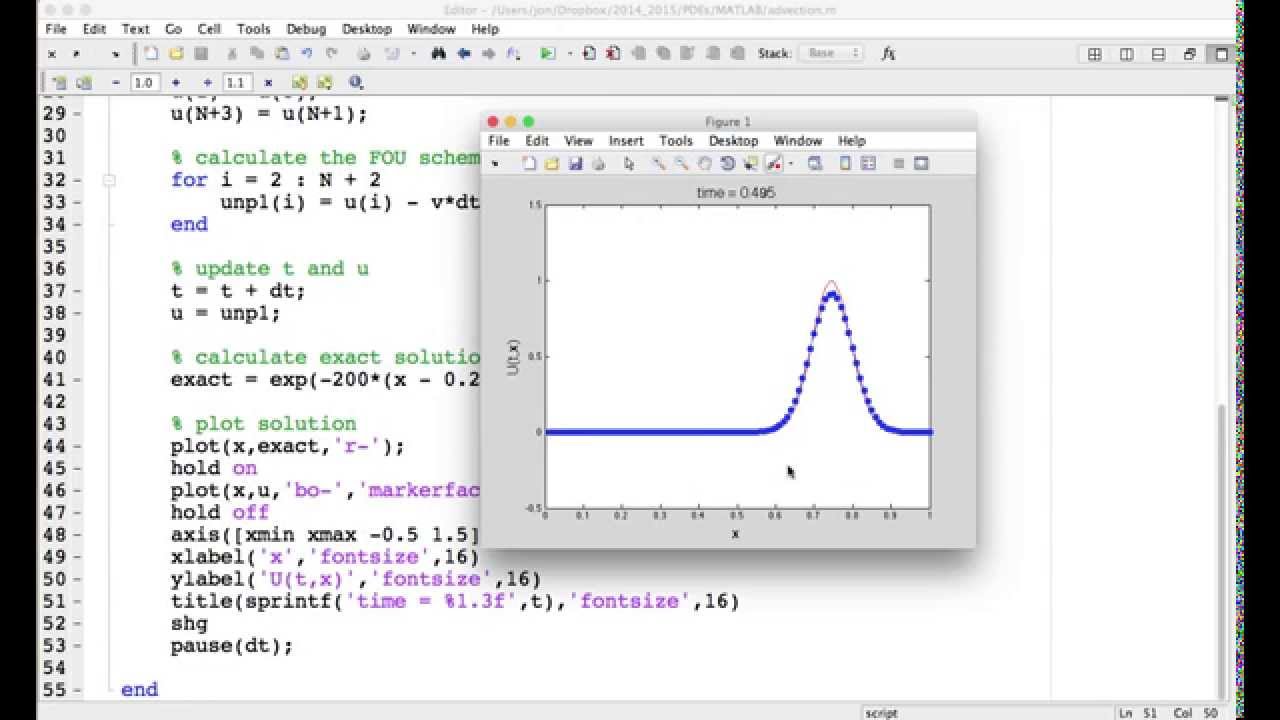
There's no need for the Symbolic Mathematics Toolbox here.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
